Skin is the largest organ in humans that is often overlooked. Skin health is often associated with beauty as having glowing healthy smooth skin is said to be attractive. Skin is more than just what it seems as it does many functions in a human life such as regulating body temperature and protecting vital organs. Skin conditions at times may or may not need attention from health services. In this article, we will learn more about a skin condition known as poikiloderma of Civatte.
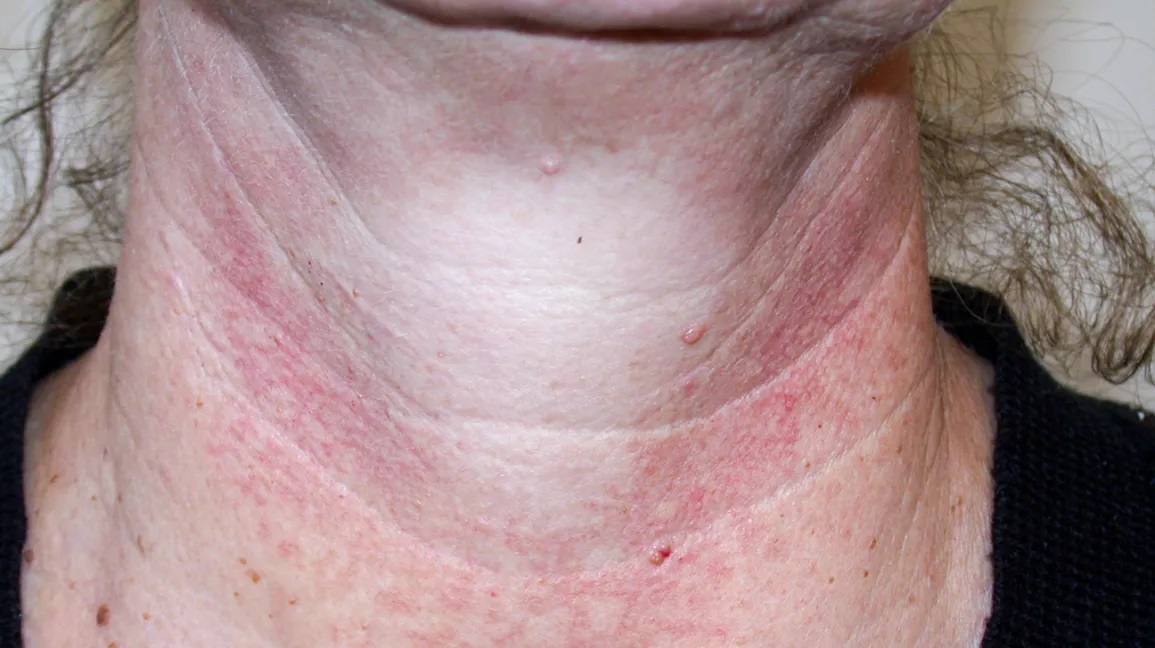
Poikiloderma of Civatte is a condition referring to the redness and mottled pigment of the neck and face. The term ‘poikiloderma’ is defined as the skin changes with atrophy (skin thinning), pigmentation changes either hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation and dilation of the fine blood vessels (telangiectasis). Poikiloderma of Civatte was first discovered back in 1923.
This skin condition is most common in middle-aged people with a tendency towards fair-skinned. Poikiloderma is also associated with sun change as the skin condition is caused by skin exposure. Long term exposure to the sun does cause skin changes on top of the normal ageing to the skin. Effects may actually be apparent as early as the person in their 20’s if a child is exposed to sun and acquired immense damage at the age of 15. Apart from long-term sun exposure to be the main cause for poikiloderma of Civatte, other causes include using cosmetics and toiletries especially perfumes, hormonal changes such as in menopause and genetic factors.
Most people with poikiloderma of Civatte do not have symptoms apart from the visible changes. Despite this, some may complain of mild burning, itching and increased sensitivity to the affected skin. Lesions that are obvious or visible with poikiloderma of Civatte are the reddish-brown patches commonly on the cheeks and neck. Poikiloderma of Civatte typically does not affect the shaded area under the chin. Sometimes it may also be the V-shaped area of the chest. Skin thinning can be found on top of pigment changes in either lightened or darkened skin with visible blood vessels as the blood vessels seem enlarged resulting from skin thinning.
The good news about poikiloderma of Civatte is there are no known medical problems associated with the skin problems. This also means that there should not be severe complications associated apart from mild itching, burning, sensitive skin and flushing at certain times. Even though there are actually similar skin lesions associated with genetic skin conditions such as connective tissue disorders and Bloom syndrome. Skin lesions similar to poikiloderma of Civatte may be seen in those who undergo radiotherapy.
Diagnosis is made based on clinical findings and several lab tests. Clinical finding of the characteristics of the skin lesion and usage of dermatoscopy is common to diagnose poikiloderma of Civatte. Lab tests are usually done to eliminate other diseases that may cause skin lesions similar to poikiloderma of Civatte. If skin lesions are not certain to be poikiloderma of Civatte, biopsy of the skin will be requested by the doctor.
There are no specific treatment for poikiloderma of Civatte but treatments are available to reduce the skin lesions. It is worth noting that the course of the skin condition is slowly progressive and irreversible. Many people who seek treatment often are those who worried of their look or for cosmetic purpose. Treatment may include lightening cream such as retinoid, alpha hydroxy acids and hydroquinone. Apart from medication in form of cream, there are option such as laser and light therapies such as pulse dye laser, intense pulse light and fractional non ablative laser. Combination of cream and laser might be used in some patient. Patients are advised to use sunscreen and protect skin with covering clothing or apparel when exposed to the sun. This is especially true when patient use lightening cream. It is recommended to avoid using perfume or cosmetics near the affected area as it may worsen the skin lesions. Patient are advised to avoid being in outdoor when the sunlight is at its peak.
Poikiloderma of Civatte is a chronic condition and is considered irreversible. Cosmetic disfigurement and poor response to treatment may be caused by the hyperpigmentation of the skin. When it is left untreated, the condition may improve with the use of sun protection. Brown areas may fade but the red area probably remains the same. Even after treatment, patients are advised to continuously protect skin from sun exposure to prevent poikiloderma of Civatte from coming back. If the skin condition does come back, maintenance laser treatment for a certain period of time may be suggested.
In essence, poikiloderma of Civatte is a harmless skin condition usually caused by long-term sun exposure to the skin. Poikiloderma of Civatte is common in middle-aged women who have fair skin. Many people do not complain of symptoms apart from the skin changes of pigments changes, skin thinning and visible blood vessels under the skin. Treatment available helps to reduce the skin lesion.