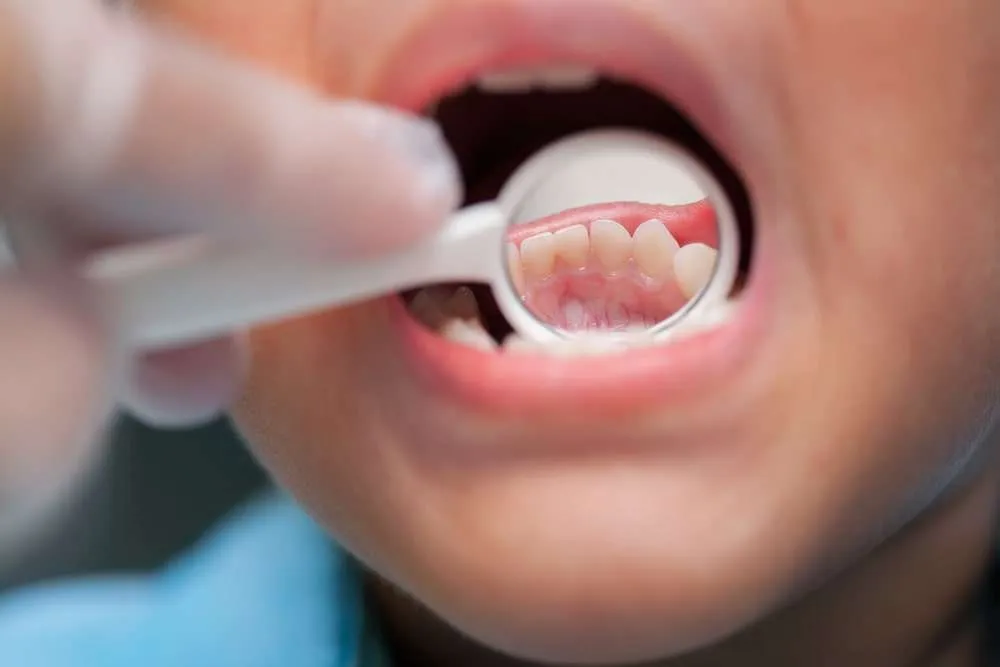
Periodontal disease can affect anyone irrespective of age and gender. Even children are not spared from this progressive destruction of gums and jawbone. Periodontal disease affecting children is known as juvenile periodontitis which is a rare form. Early detection and treatment help prevent further complications that may affect the budding or newly erupted permanent teeth.
Dental specialists offer comprehensive periodontal treatment in Dieppe, NB, for juvenile periodontitis, but first let’s understand the causes and signs of this gum disease.
What is periodontitis?
Periodontitis, gum or periodontal disease, is a severe and advanced stage of gum inflammation. It is a chronic bacterial infection that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone.
What causes juvenile periodontitis?
Typically, plaque accumulation due to increased bacterial infiltration causes periodontitis. Failure to remove the plaque through proper hygiene practices like brushing, flossing, and regular dental cleanings may harden into calculus, which allows bacteria to thrive. As the bacteria grow, they produce toxins and acids that irritate your gums leading to inflammation (gingivitis), which may progress to periodontitis.
The following factors may contribute to the development of juvenile periodontitis:
-
Genetic predisposition
-
-
- Having a family member with periodontal disease due to improper immune response
-
-
Poor oral hygiene
-
-
- Improper brushing and flossing can result in increased plaque accumulation and bacterial colonization.
-
-
Impaired immune response
-
-
- Children with compromised immune systems or having any underlying medical condition like juvenile diabetes or anemia may be more susceptible to periodontitis.
- An impaired immune system makes it harder for the body to fight off infections and control inflammation.
-
-
Other factors
-
- Poor nutrition and puberty may be other factors that contribute to the progression of these conditions.
What are the signs of juvenile periodontitis?
Signs and symptoms of juvenile periodontitis include:
- Red, swollen, and bleeding gums
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Tender and painful gums
- Receding gums
- Formation of deep periodontal pockets
- Loose teeth
- Malocclusion (bite changes)
- Pain while chewing
- Pus between teeth and gums
How to treat juvenile periodontitis?
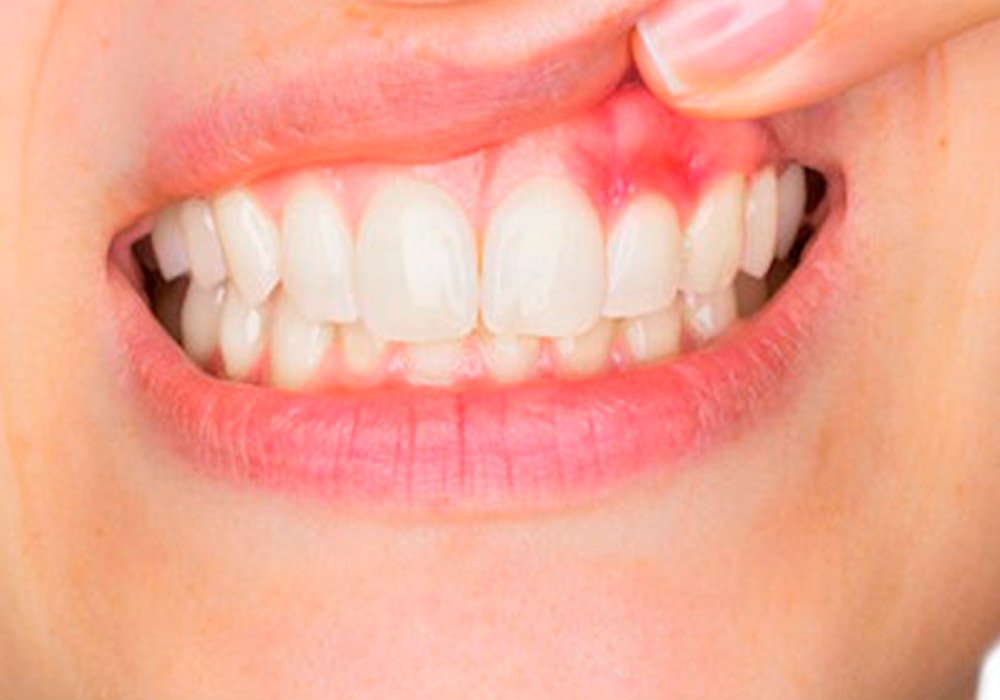
Treatment depends on your child’s age, symptoms, and general health.
Options may include any one or a combination of the following:
- Regular brushing and flossing
- Using a fluoride toothpaste
- Eating a well-balanced diet
- Regular dental visits for deep cleanings which may include scaling and root planing
- Antibiotic medicine may be put in the periodontal pockets
- Surgery for advanced periodontitis where the gum tissues may be reshaped and replaced.
Takeaway
You need to keep a check on your child’s oral health. Having good oral hygiene habits from a young age can keep oral problems like gum disease and periodontitis at bay. It may not be easy to get kids and teens on board with good oral hygiene, but it will all be worth it every time you see their happy and healthy smiles.